
UEFI runs in 32-bit or 64-bit mode, while BIOS operates in 16-bit mode. Therefore, it offers greater scalability, better performance, programmability, and security. UEFI is a newer firmware developed for more recent machines. System initialization information stored in a. System initialization information stored in a dedicated chip on the motherboard. Provides a user-friendly graphical UI with mouse support.įaster boot time and better performance compared to BIOS. The table below compares some of the key features of BIOS and UEFI:
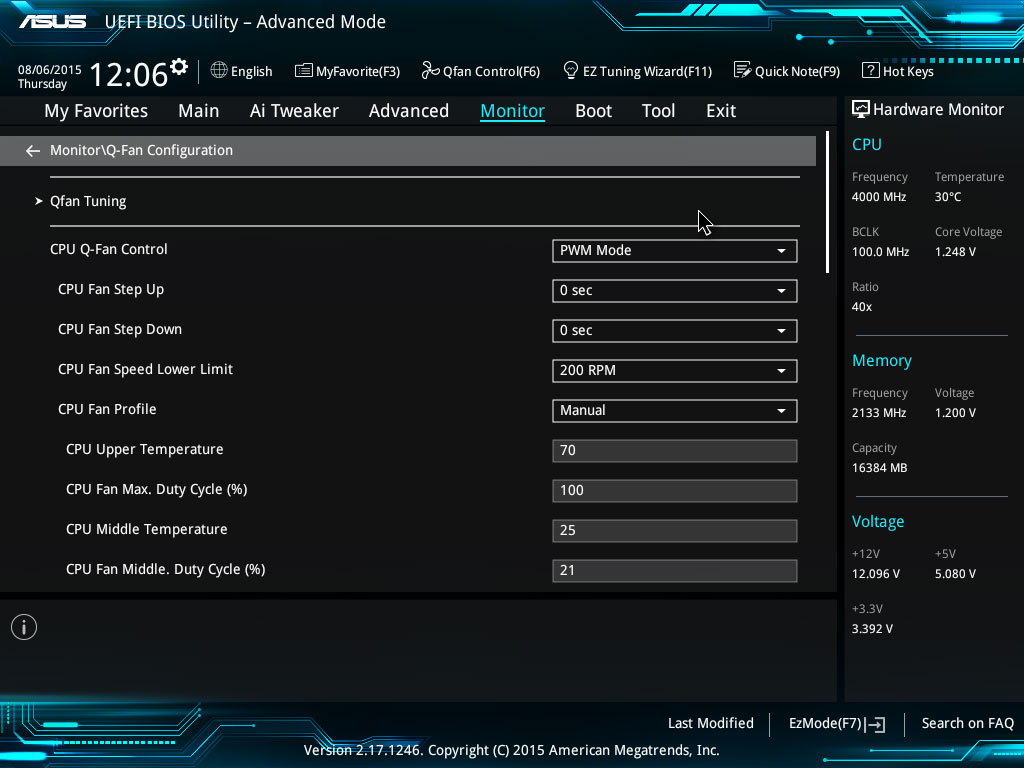
UEFI: DifferencesĪlthough BIOS and UEFI are both used to kickstart the machine hardware before the operating system loads, there are some key differences between the two solutions. The image below shows an example of BIOS: BIOS vs. The firmware uses the MBR partitioning scheme and supports up to 2 TB storage devices.

After performing the device checks, BIOS looks for bootable devices and hands over control to the OS.īIOS works in 16-bit mode, which also limits the amount of code that can be read and executed from the firmware ROM. The purpose of BIOS is to check settings stored in a CMOS chip to determine how the user wants the system to run and which devices to initialize - CPU, GPU, RAM, etc. The chip is non-volatile, meaning it retains its contents even after the power is turned off.
It is a small piece of code on a read-only flash memory chip on the motherboard called EPROM (Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory). BIOS stands for Basic Input/ Output System.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
